I still remember my first IPO application. The excitement was real. A new company, fresh opportunity, and the feeling that I might be part of something big from day one. At the same time, I was confused. What exactly is an IPO? How does it work? And most importantly—how do you invest safely?
If you have similar questions, you’re in the right place. This article explains what is IPO in finance and how to do it, starting from the basics and moving gradually to an intermediate level.

What is IPO in finance? Learn how IPOs work, how to apply, risks, benefits, and smart ways to invest in IPOs.
What Is IPO in Finance?
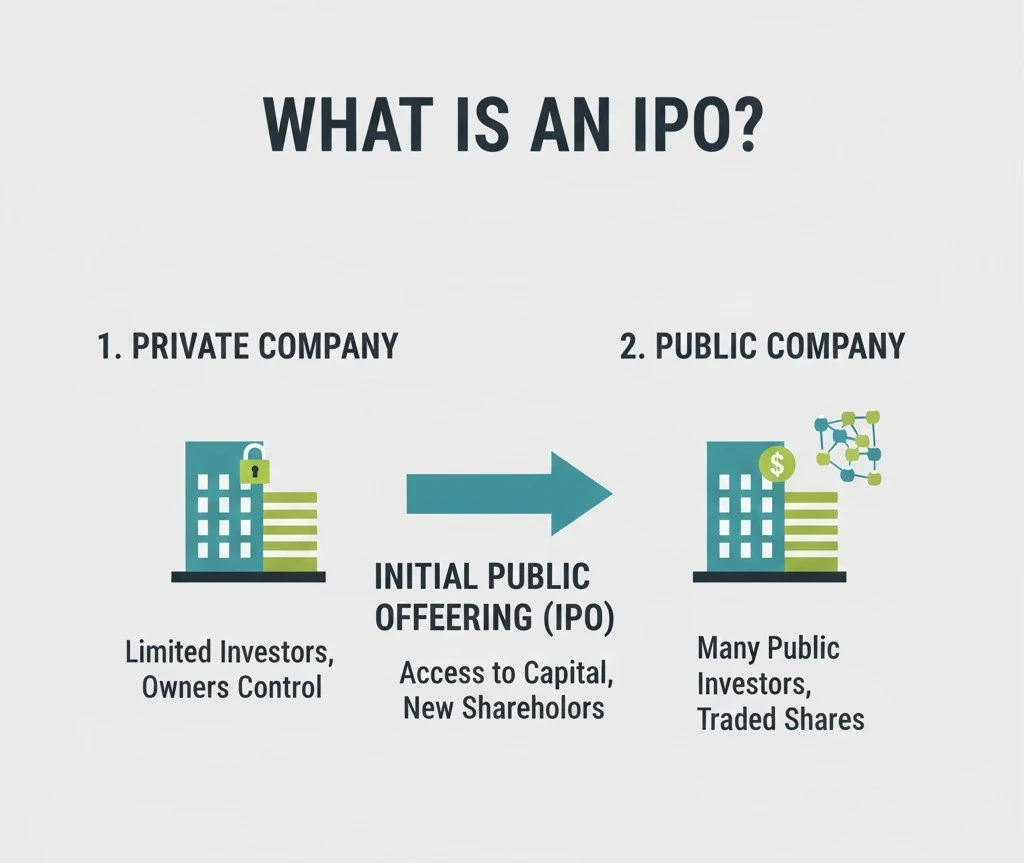
IPO stands for Initial Public Offering. It is the process through which a private company offers its shares to the public for the first time and gets listed on a stock exchange.
In simple words, an IPO is when a company says:
“We are ready to let the public own a part of our business.”
After an IPO, anyone with a demat account can buy and sell the company’s shares in the stock market.
Why Companies Launch an IPO
Companies go public for several reasons:
- To raise money for growth
- To expand business operations
- To reduce existing debt
- To increase brand visibility
- To give early investors an exit
An IPO helps a company move from private ownership to public ownership.
How IPO Works: Step-by-Step Process
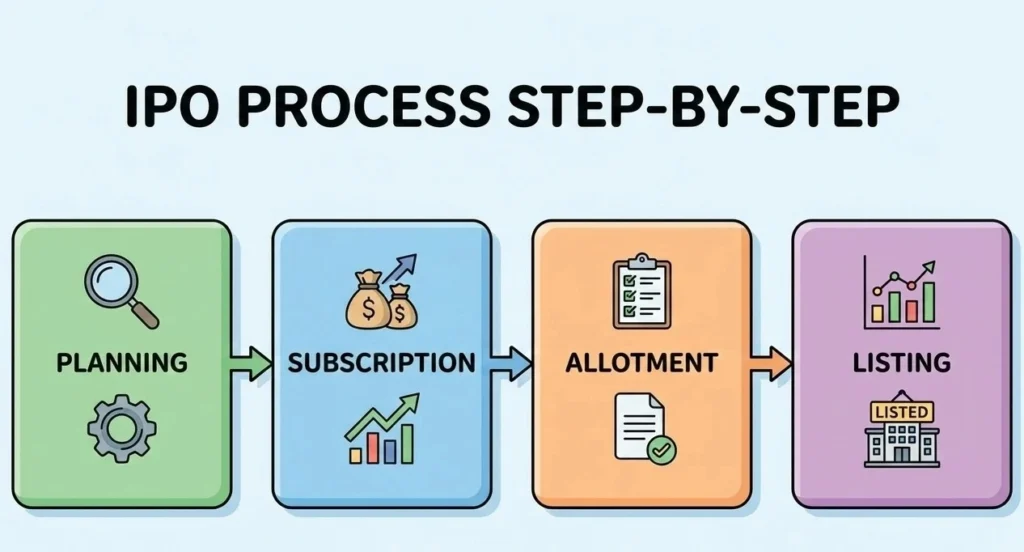
Understanding the IPO process removes fear and confusion.
1. Company Planning
The company decides to go public and appoints investment banks.
2. Regulatory Approval
Documents are submitted to market regulators for approval.
3. Price Band Announcement
The company sets a price range for shares.
4. Public Subscription
Investors apply for shares during the IPO window.
5. Allotment
Shares are allotted based on demand.
6. Listing
The company’s shares start trading on the stock exchange.
Types of IPOs
Fixed Price IPO
The share price is fixed in advance.
Book Building IPO
The price is decided based on investor demand within a price band.
Book building IPOs are more common today.
Who Can Invest in an IPO?
Almost anyone can invest in an IPO if they have:
- A demat account
- A trading account
- A linked bank account
Investors are usually divided into:
- Retail investors
- High net-worth individuals
- Institutional investors
How to Apply for an IPO

Applying for an IPO is simple today.
You can apply using:
- Online trading apps
- Bank ASBA facility
Steps:
- Log in to your trading platform
- Select the IPO
- Enter quantity and price
- Submit application
Funds are blocked and released if shares are not allotted.
IPO Allotment: How It Works
If demand is high, IPOs become oversubscribed.
In such cases:
- Shares are allotted via lottery system (for retail)
- Many applicants may not receive shares
This is normal and part of the process.
IPO Listing Day: What Happens?
On listing day:
- Share price opens on exchange
- Price may go up, down, or stay flat
Some investors sell immediately for listing gains, while others hold for long-term growth.
Benefits of Investing in IPOs
- Early entry into growing companies
- Potential listing gains
- Opportunity to invest at initial valuation
However, benefits come with risks.
Risks Involved in IPO Investment

IPO investing is not risk-free.
Common risks include:
- Overvaluation
- Limited company history
- Market volatility
- Emotional decision-making
Understanding risk management is essential before applying.
IPO vs Regular Stock Market Investment
IPO investing focuses on new listings.
Stock market investing focuses on already listed companies.
Both have different strategies and risk profiles.
How to Analyze an IPO Before Investing
Before applying, check:
- Company business model
- Revenue and profit growth
- Debt levels
- Industry outlook
- Purpose of IPO
Avoid investing only based on hype.
IPO and Risk Management
Never invest all capital in IPOs.
Smart practices include:
- Limited allocation
- Diversification
- Clear exit plan
Risk management protects long-term wealth.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make in IPOs
- Chasing hype
- Ignoring fundamentals
- Investing borrowed money
- Expecting guaranteed listing gains
Patience beats excitement.
IPOs in the Long Term
Not all IPOs are for short-term gains.
Some companies create value slowly over years. Long-term investors benefit by staying disciplined.
Final Thoughts

Understanding what is IPO gives you confidence as an investor. IPOs are powerful tools for wealth creation when approached with knowledge, patience, and discipline.
Start small. Learn continuously. Protect capital.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is IPO good for beginners?
Yes, if beginners understand risks and invest carefully.
Can I lose money in IPOs?
Yes. IPO prices can fall after listing.
How much money is needed to apply for an IPO?
Only the minimum application amount.
Are IPO profits guaranteed?
No. There are no guarantees in markets.

